

Postganglionic fibers innervate the pupillary sphincter muscles. After synapsing in the ciliary ganglia (CG), the 3 Preganglionic parasympathetic fibers ( heavy dashed lines) leave ventral aspect of midbrain in the substance of the third cranial Neurons to both Edinger–Westphal parasympathetic motor nuclei (E–W), which comprise the dorsal aspect of the oculomotor The PTN is connected by crossed and uncrossed intercalated Geniculate nucleus (LGN) is bypassed by these pupillomotorįibers. Terminate in pretectal nuclear complex (PTN). Light in left eye ( dotted arrow) stimulates retina (RET), whose afferent axons ( fine dashed lines) ascend optic nerve (ON), decussate at chiasm (CHI), and Iris color, on the other hand, may affectĬonstriction amplitude and velocity but not pupillary size. Occipital cortex above the pretectal area and from the reticular formation Light adaptation, and supranuclear influences from the frontal and Retinal illumination, the near-effort reflex, the state of retinal 2 In addition, the size of the pupils is influenced by the intensity of Pupillary size directly by dilator muscle innervation or indirectlyīy central inhibition of the oculomotor parasympathetics (Edinger-Westphal Outflow to the pupillary sphincter and ciliary muscle and (6) theĮfferent sympathetic pathway from the hypothalamus In the oculomotor nuclear complex (5) the efferent parasympathetic Of the superior colliculus (4) pretectal area of the mesencephalonĪnd the interconnecting neurons to pupilloconstrictor motor cells
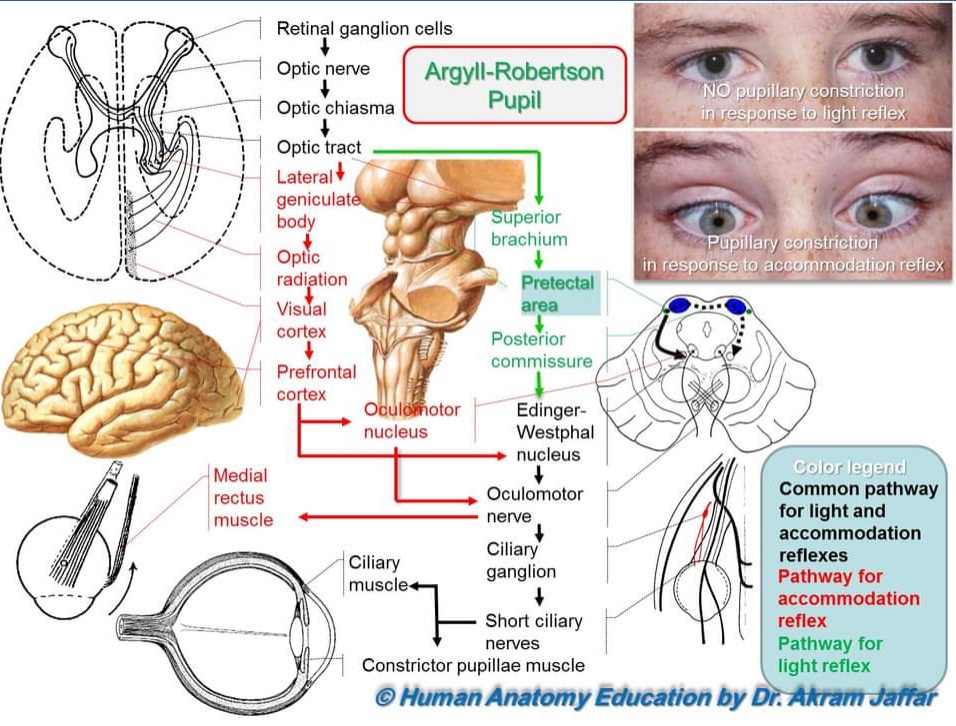
Not the lateral geniculate body) (3) brachium These include: (1) retinal receptors (2) ganglionĬell axons in the optic nerve, optic chiasm, and optic tract (but Pupillary function depends on the integrity of the structures along theĬourse of the pupillomotor pathway ( Fig. Loewenfeld's scholarly text, The Pupil: Anatomy, Physiology and Clinical Applications, is recommended reading for encyclopedic information about the pupil.
They may be sampled and evaluated by simple clinical procedures. That control pupil size and reactivity are highly complex, yet The retina, the special sensory apparatus that it serves. The pupil is a kinetic indicator of both ocular motor function and the Protecting them like the pupil* of His eye. Here, the clinical manifestations, pathogenesis, relationship between Adie's pupil and diseases, and differential diagnosis of Adie's pupil are reviewed.Volume 2, Chapter 15. Differential diagnosis between Adie's pupil, oculomotor nerve palsy, anticholinergic drug overdose, Argyll-Robertson pupil, and congenital mydriasis need to be identified by the physician. It is essential for clinicians to improve their understanding of the disease to avoid misdiagnosis. Pilocarpine can be used to treat ophthalmologic symptoms, such as blurred vision, for which patients might visit an ophthalmologist or neurologist. The ophthalmological symptoms and pupil abnormalities can disappear after active treatment of the primary disease. Through a literature review, we found that Adie's pupil is mainly associated with infectious diseases, most commonly syphilis, followed by immune diseases and paraneoplastic syndromes. The pathogeneses of Adie's pupil are complex, some of which are insidious and lack corresponding specific diseases. The pupil on the affected side is sensitive to low concentrations of pilocarpine. The direct and indirect light reflection from the pupil on the affected side disappears. The pupil of the affected side is significantly larger than that on the healthy side. Most patients have unilateral eye involvement.
Adie's pupil, also called tonic pupil, is mainly seen in young women.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
